Understanding Blood Pressure: Causes, Effects, and Management
Learn about the causes, effects, and management of blood pressure. Get valuable health insights with Breaking Way.
What is Blood Pressure?
Blood pressure refers to the force exerted by circulating blood against the walls of the arteries. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and consists of two numbers:
- Systolic Pressure: The pressure when the heart beats and pumps blood.
- Diastolic Pressure: The pressure when the heart rests between beats.
A normal blood pressure reading is typically around 120/80 mmHg. Readings consistently above or below this range can signal health issues that need attention.
Causes of High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
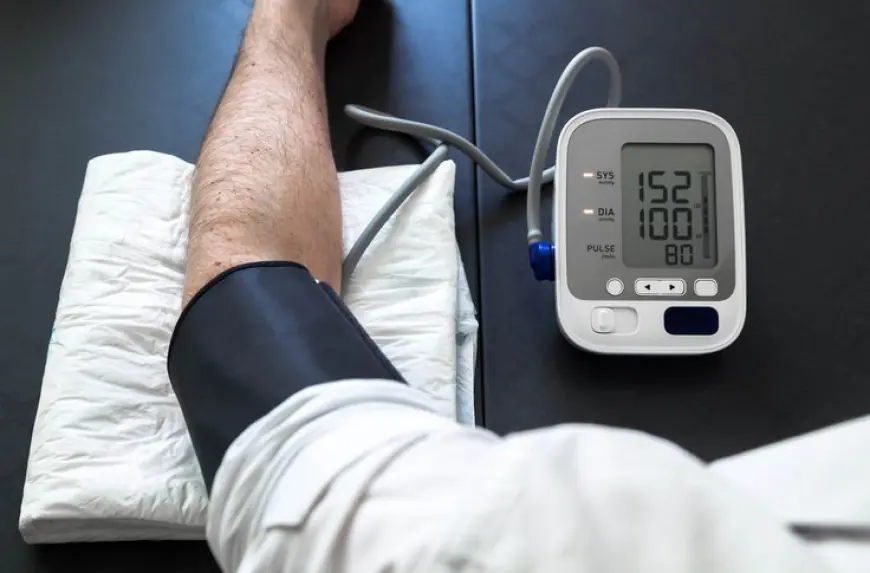
High blood pressure, or hypertension, affects nearly 1.28 billion adults worldwide, according to the World Health Organization. Common causes include:
- Genetics: A family history of hypertension increases your risk.
- Dietary Habits: High salt intake, excessive alcohol consumption, and a diet low in potassium.
- Obesity: Excess weight forces the heart to work harder, increasing pressure.
- Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle contributes to weight gain and hypertension.
- Chronic Stress: Continuous stress can elevate blood pressure.
- Smoking: Tobacco use damages blood vessels and raises blood pressure.
Effects of High Blood Pressure
Hypertension can lead to severe health complications, including:
1. Heart Disease: It is a major risk factor for heart attacks and heart failure.
2. Stroke: Increased pressure can lead to blockages or bleeding in the brain.
3. Kidney Damage: High blood pressure can damage the blood vessels in the kidneys, affecting their ability to filter waste.
4. Vision Problems: Can cause damage to the retina, leading to vision loss.
5. Aneurysms: Elevated pressure can cause the arteries to bulge, potentially leading to life-threatening ruptures.
Causes of Low Blood Pressure (Hypotension)

While less common, low blood pressure, or hypotension, can also present health risks. Causes include:
- Dehydration: Lack of fluids can lead to decreased blood volume.
- Heart Issues: Some heart conditions can result in low blood pressure.
- Endocrine Disorders: Problems with hormone-producing glands can cause hypotension.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Deficiencies in vitamins such as B12 and folate.
- Medications: Certain medications, including diuretics and antidepressants, can lower blood pressure.
Effects of Low Blood Pressure
Low blood pressure can result in:
- Dizziness and Fainting: Reduced blood flow to the brain can cause lightheadedness.
- Fatigue: Insufficient blood flow can lead to tiredness and weakness.
- Blurred Vision: Poor circulation may affect vision temporarily.
How to Measure Blood Pressure
Monitoring blood pressure is crucial for early detection and management. You can measure your blood pressure at home using a digital monitor or have it checked by a healthcare provider. Regular monitoring helps track your progress and adjust management strategies as needed.
Managing Blood Pressure
Effective management of blood pressure involves lifestyle changes and possibly medication:
1. Adopt a Healthy Diet: Follow the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, which includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Limit salt and processed foods.
2. Exercise Regularly: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise, such as brisk walking, per week.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight: Losing even a small amount of weight can significantly lower your blood pressure.
4. Limit Alcohol and Quit Smoking: Both alcohol and tobacco can raise blood pressure and harm blood vessel health.
5. Manage Stress: Use techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing to reduce stress.
6. Monitor Your Blood Pressure: Regular monitoring can help detect changes early, allowing for timely intervention.
When to Seek Medical Help?

If you experience persistent symptoms like severe headaches, chest pain, shortness of breath, or frequent dizziness, consult a healthcare professional immediately. Consistent monitoring and professional guidance are essential for managing blood pressure effectively.
Take control of your blood pressure today. Start by implementing small lifestyle changes and regularly monitor your levels. For personalized advice, consult with a healthcare provider.
Conclusion
Managing blood pressure is key to preventing serious health issues and maintaining overall well-being. By understanding the causes and effects of blood pressure fluctuations and adopting a proactive approach, you can effectively control your blood pressure and improve your quality of life.
Sources
1. American Heart Association. "Understanding Blood Pressure Readings." [American heart association]
2. Mayo Clinic. "High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)." [Mayo Clinic]
3. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. "What Is High Blood Pressure?" [NHLBI]
4. Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. "The Nutrition Source: Healthy Eating Plate." [Harvard Nutrition]
What's Your Reaction?