Managing Diabetes in Older Adults : A Comprehensive Guide
how to effectively manage diabetes in older adults with expert tips on care, diet, and treatment. Get insights from Breaking Way Health.

What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects how the body processes sugar (glucose), which is the main source of energy for cells. In diabetes, there is a problem with the production or use of insulin, a hormone crucial for regulating blood glucose levels. There are two primary types of diabetes:
1. Type 1 Diabetes:
This type occurs when the pancreas fails to produce insulin altogether. It is typically diagnosed in younger individuals and requires lifelong insulin therapy.
2. Type 2 Diabetes:
This type occurs when the pancreas does not produce enough insulin or when the body cannot effectively use insulin. It is more common in adults, especially older adults, and can often be managed with lifestyle changes, medication, or insulin.
Importance of Exercise for Older Adults
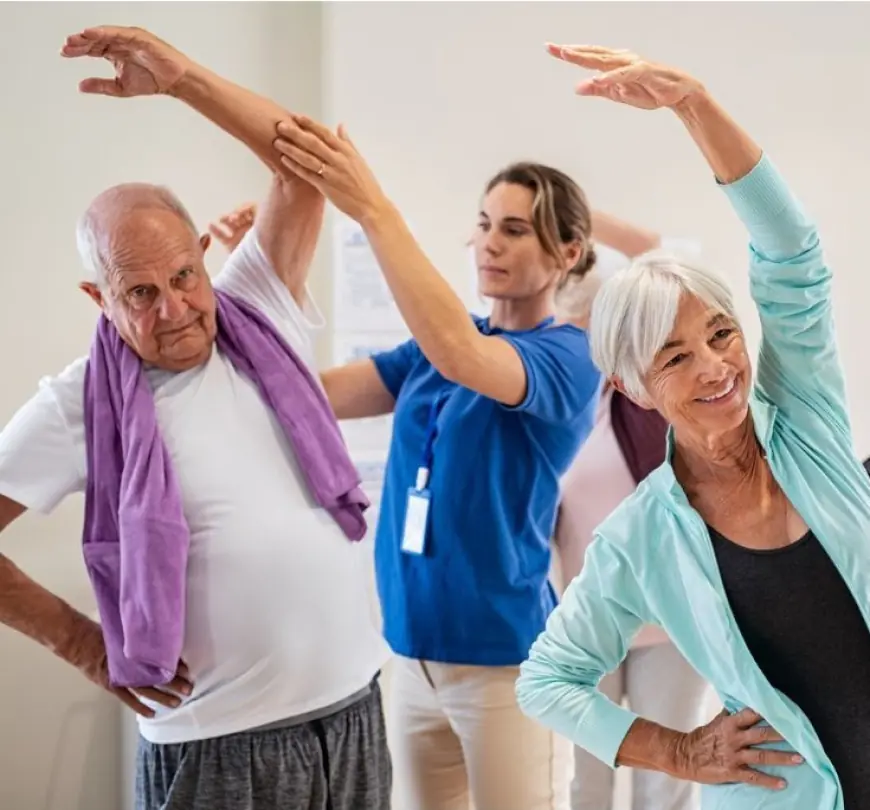

Regular physical activity is essential for managing diabetes in older adults. Exercise improves insulin sensitivity, helps control weight, and supports overall cardiovascular health. Recommended activities include:
-Walking: A low-impact exercise that can be easily incorporated into daily routines.
-Swimming: Provides a full-body workout with minimal stress on the joints.
-Cycling: Enhances cardiovascular health and builds muscle strength.
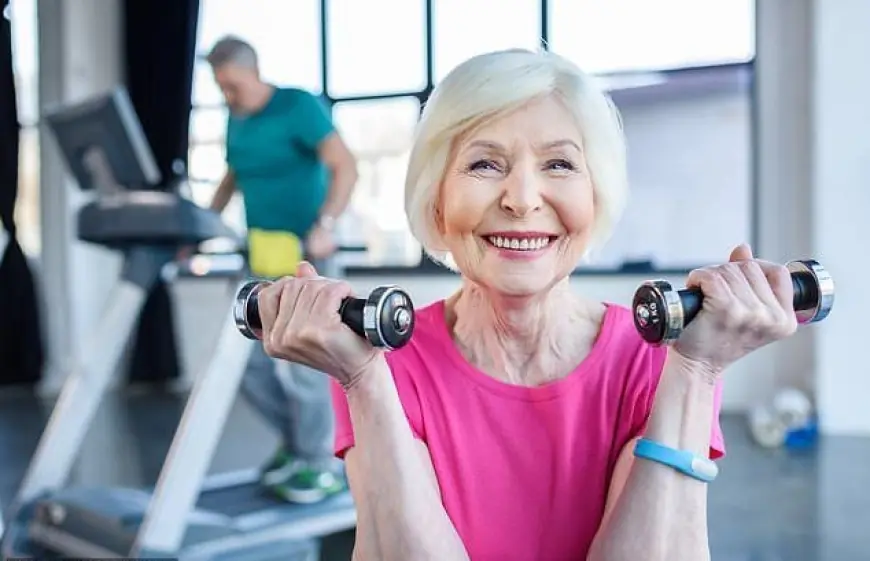

In addition to structured exercises, everyday activities like gardening or climbing stairs also contribute to physical fitness. Older adults need to start with low-intensity activities and gradually increase intensity, taking into account any existing health conditions.
Balanced Diet

A balanced diet plays a crucial role in diabetes management. Older adults should aim to:
- Include a variety of nutrients: Incorporate proteins, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates.
- Focus on fiber-rich foods: Such as vegetables, fruits, and whole grains to help manage blood glucose levels.
- Avoid refined sugars and processed foods: These can cause rapid spikes in blood glucose levels.
Eating regular, balanced meals and snacks can help maintain stable blood glucose levels throughout the day.
Importance of Regular Check-ups
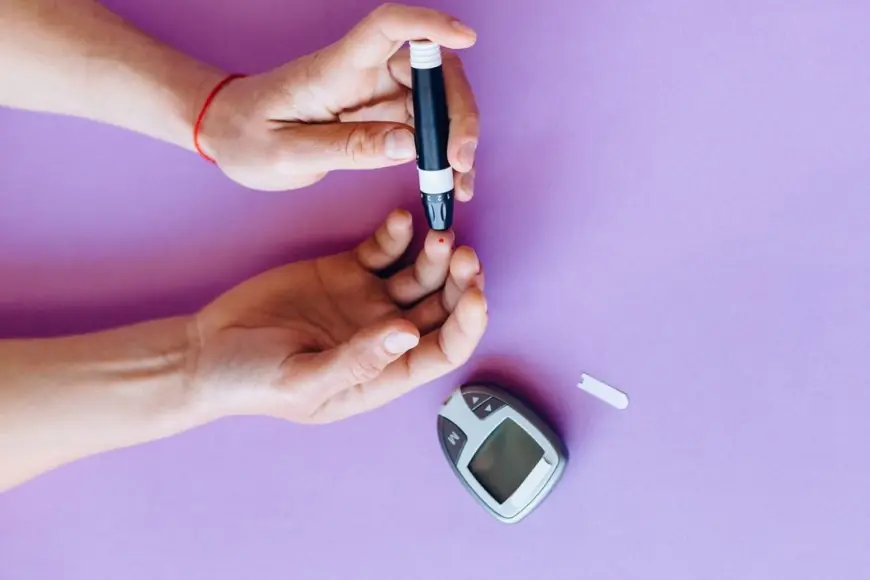

Regular medical check-ups are vital for monitoring diabetes and preventing complications. Key components of regular monitoring include:
- Blood glucose levels: Regular testing helps ensure that blood sugar levels are within the target range.
- Cholesterol and blood pressure: High levels can increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
- Eye and kidney exams: Diabetes can affect these organs, so regular screenings are necessary to detect any problems early.
Recognizing and Managing High and Low Blood Sugar Symptoms
High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia):
Symptoms include excessive thirst, frequent urination, fatigue, and unexplained weight loss. Managing high blood sugar involves:
- Measuring blood glucose levels: Regular checks can help in managing and adjusting treatment as needed.
- Taking prescribed medications: Following the doctor's recommendations for medication or insulin use.
- Seeking medical help: In severe cases or if symptoms persist, it may be necessary to seek immediate medical care
Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia):
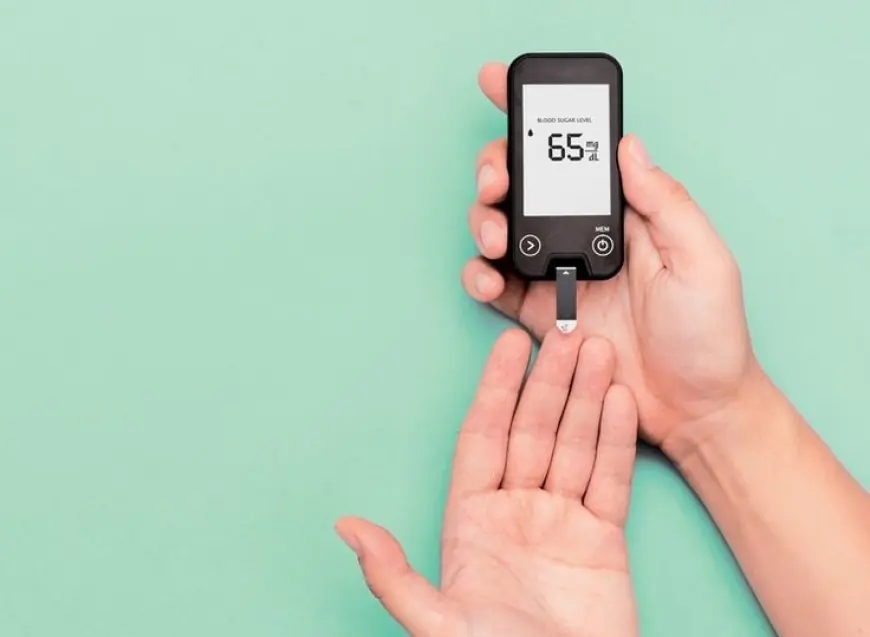

Symptoms may include dizziness, sweating, shaking, and confusion.
To address low blood sugar:
- Consume fast-acting carbohydrates: Such as fruit juice or candy, to quickly raise blood glucose levels.
- Monitor blood sugar levels: Regular checks can help prevent and manage low blood sugar episodes.
- Consult a doctor: If symptoms are severe or recurrent, medical advice should be sought.
Conclusion
This comprehensive guide provides valuable insights and practical tips for managing diabetes in older adults, ensuring they can lead healthier and more fulfilling lives.
About diabetes look also https://breakingway.com/diabetes-understanding-its-type-symptoms-and-treatment
References
1. American Diabetes Association (ADA)."Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2023." Diabetes Care, vol. 46, Supplement 1, 2023, pp. S1-S291.
2. Morrish, N. J., et al. "The Effect of Lifestyle Modification on Glycemic Control in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Review of the Evidence." Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice, vol. 134, 2018, pp. 53-62.
3. National Institute on Aging (NIA). "Managing Diabetes in Older Adults." National Institute on Aging, 2022, www.nia.nih.gov
4. U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). "Physical Activity and Older Adults." CDC, 2023, www.cdc.gov
5. World Health Organization (WHO). "Diabetes." WHO, 2023, www.who.int
What's Your Reaction?