Diabetes: Understanding Its Types, Symptoms, and Treatments
The different types of diabetes, common symptoms, and treatment options. Get expert insights with Breaking Way Health.
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels due to the body's inability to produce enough insulin or use insulin effectively. It is one of the most common and widespread diseases globally. In this article, we will explore the types of diabetes, the characteristics of each type, and the best treatment methods.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a condition that impacts the body's metabolism, specifically its capacity to manage glucose (sugar). Insulin, a hormone generated by the pancreas, is vital for controlling how cells use glucose to produce energy. In diabetes, this process is impaired, causing a build-up of sugar in the bloodstream.
Types of Diabetes :
1. Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes occurs when the immune system attacks the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas, leading to the accumulation of glucose in the blood. This type of diabetes commonly affects children and young adults before puberty. Insulin therapy is essential for managing this type of diabetes.
2. Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes happens when the body becomes resistant to insulin, leading to its ineffective use and resulting in elevated blood sugar levels. This type of diabetes is the most common, typically affecting adults over the age of 40, but can also occur at a younger age due to factors like obesity and lack of physical activity also Genetic Factors If one or both parents have Type 2 diabetes, the risk of developing the disease increases.
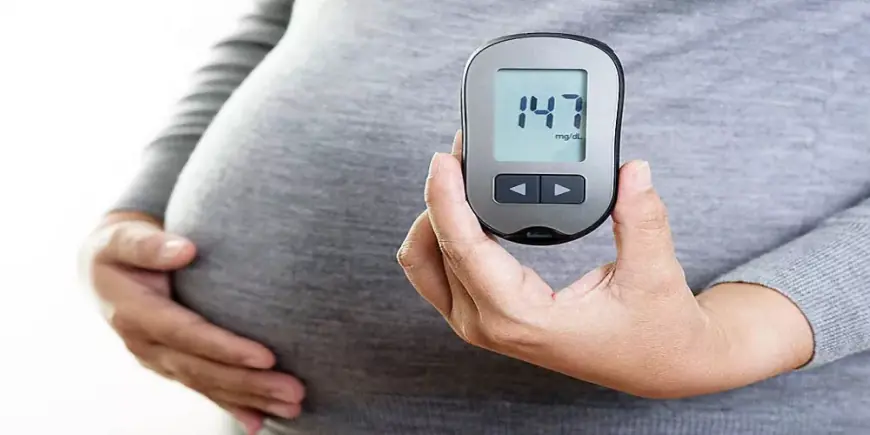

3. Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a temporary type of diabetes that occurs during pregnancy due to hormonal changes. It happens when the pancreas cannot produce enough insulin to meet the increased demands during pregnancy. Although temporary, gestational diabetes can pose risks to both the mother and the baby, requiring careful monitoring.
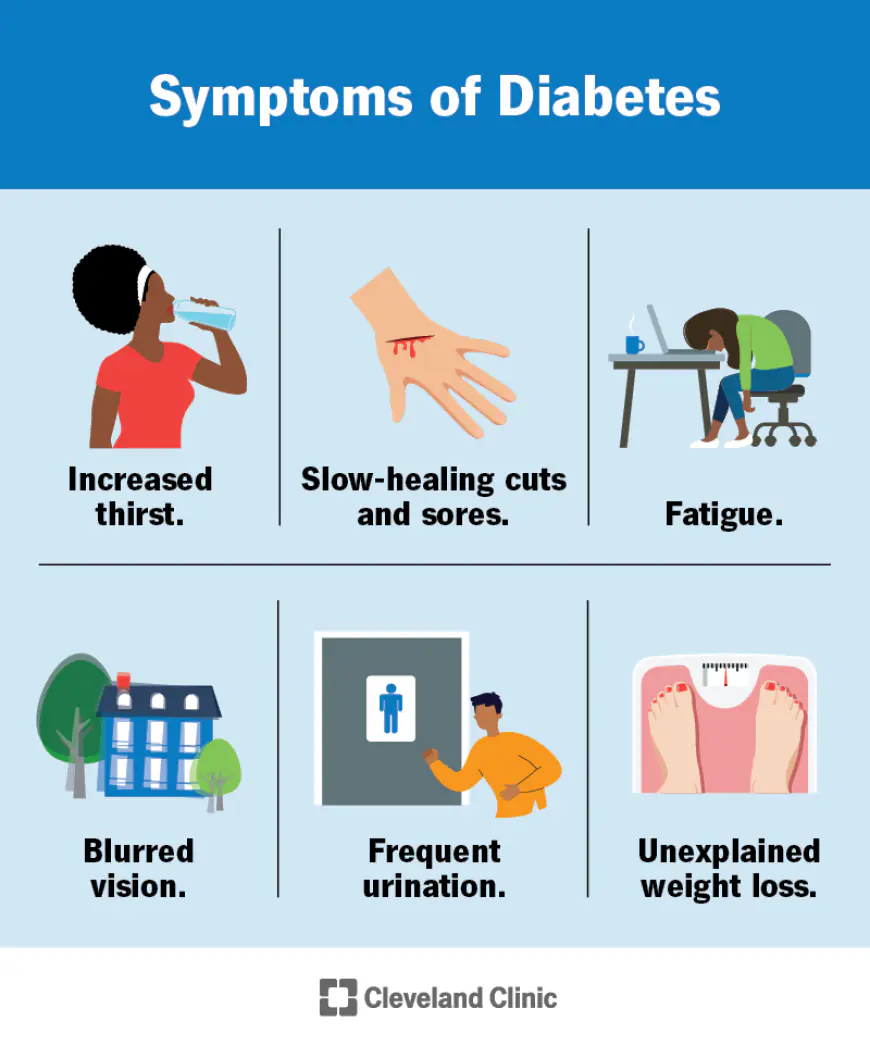
Symptoms of Diabetes :
Identifying the early signs of diabetes is essential for prompt diagnosis and treatment. These signs and Symptoms include:
- Persistent thirst
- Frequent urination
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue and general weakness
- Slow healing of wounds
- Blurred vision
- Increased susceptibility to infections
How to Diagnose Diabetes?
Diabetes diagnosis is based on the presence of symptoms along with specific laboratory tests, such as:
- Random blood sugar level: Over 200 mg/dL
- Fasting blood sugar level: Over 126 mg/dL
- Blood sugar level two hours after eating: Over 200 mg/dL
- HbA1c level: Over 6.5%
In the absence of symptoms, additional tests may be required to confirm the diagnosis, as a single reading may not be sufficient.

Diabetes Treatment :
Diabetes treatment depends on the type of diabetes and blood sugar levels. Below is an overview of the treatments used for each type:
Treatment for Type 1 Diabetes :
Type 1 diabetes is typically managed with insulin injections or an insulin pump. Patients also need to monitor their blood sugar levels regularly and count carbohydrates in their diet. In some cases, pancreas or islet cell transplants may be considered.
Treatment for Type 2 Diabetes :
Type 2 diabetes treatment often involves lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet and engaging in regular physical activity. This may be supplemented with oral diabetes medications, insulin, or both.

Tips for a Healthy Lifestyle :
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is crucial for managing diabetes effectively. Here are some tips to help:
- Choose healthy foods: Focus on consuming fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. These foods are rich in fiber and low in fat and calories. It's important to reduce the intake of saturated fats, refined carbohydrates, and sweets. Occasional indulgence in sugary foods is acceptable, but they should be accounted for in your dietary plan. A dietitian can help you determine the appropriate portion sizes.
- Engage in regular physical activity: Physical activities don't need to be strenuous. A 30-minute walk or any preferred activity daily is sufficient.
- Monitor your blood sugar regularly: Regularly check your blood sugar levels according to your treatment plan to help manage diabetes effectively.
Proper management of diabetes through lifestyle changes, medication, and regular blood sugar monitoring is essential to prevent complications. Continuous medical consultation is also crucial to ensure the effectiveness of the treatment.
What's Your Reaction?