Understanding Mental Disorders: Types, Causes, and Treatments
The different types of mental disorders, their causes, and available treatments. Gain insights with Breaking Way Health.

Types of Mental Disorders
Mood Disorders:
Such as major depression and bipolar disorder, where emotions and mood are significantly affected, with periods of deep sadness or mania.
Anxiety Disorders:
Including generalized anxiety, panic disorders, and social anxiety disorders. These conditions involve recurring feelings of intense tension and anxiety.
Eating Disorders:
Including binge-eating disorder, anorexia nervosa, and bulimia nervosa. These disorders involve unhealthy relationships with food and body weight.
Schizophrenia:
A condition affecting fundamental thinking and perception, leading to cognitive and social interaction disturbances.
Causes of Mental Disorders
Mental disorders are influenced by multiple factors including genetics, environment, and psychological factors. Life stressors, psychological trauma, and chemical imbalances in the brain can increase the risk of developing mental disorders.
Treatment of Mental Disorders


Medication:
Involves the use of scientifically approved medications to alleviate symptoms and improve the patient's quality of life.
Therapy:
Includes cognitive-behavioural therapy and modern therapies focusing on promoting positive thinking and improving emotional responses.
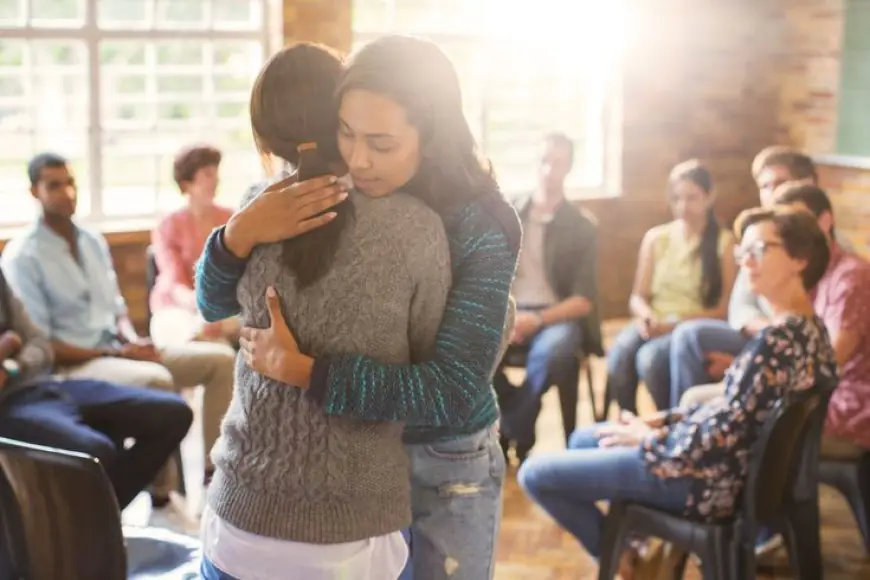
Social Support:
Plays a vital role in helping patients cope with their conditions and providing the necessary support during difficult times.
Expanding on Mental Health Challenges
Understanding mental health challenges requires a nuanced approach that addresses the complexities of the human mind. The following section explores each type of mental disorder in detail, providing insights into their symptoms, risk factors, and treatment options.
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) is characterized by persistent and excessive worry about everyday things. Individuals with GAD often anticipate disaster and may be overly concerned about health issues, money, family problems, or difficulties at work. Symptoms include restlessness, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, irritability, muscle tension, and sleep disturbances.
Risk factors for GAD include genetics, brain chemistry, personality, and life experiences. While the exact cause of GAD is unknown, it is believed to involve a combination of biological, psychological, and environmental factors.
Treatment for GAD typically includes a combination of medication and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT). Medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) can help alleviate symptoms. CBT focuses on identifying and challenging irrational thoughts and behaviours that contribute to anxiety.
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD)
Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) is characterized by a persistent feeling of sadness or loss of interest in activities that were once enjoyed. Symptoms of MDD include changes in appetite or weight, sleep disturbances, fatigue or loss of energy, feelings of worthlessness or guilt, difficulty concentrating, and thoughts of death or suicide.
Risk factors for MDD include genetics, biological factors, personality traits, and life events such as trauma, loss of a loved one, or chronic stress. Imbalances in neurotransmitters like serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine are also associated with MDD.
Treatment for MDD often involves a combination of antidepressant medications, psychotherapy, and lifestyle changes. Antidepressants such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) are commonly prescribed to help regulate neurotransmitter levels. Psychotherapy, particularly cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) and interpersonal therapy (IPT) can help individuals identify negative thought patterns and improve coping strategies.
Bipolar Disorder
Bipolar Disorder is a mood disorder characterized by extreme mood swings that include emotional highs (mania or hypomania) and lows (depression). Symptoms of mania include increased energy, euphoria or irritability, racing thoughts, reduced need for sleep, grandiose ideas, and impulsive behaviours. Symptoms of depression in bipolar disorder are similar to those in MDD.
Conclusion
Mental disorders are not insurmountable obstacles. With deep understanding and appropriate support, individuals affected by these disorders can lead stable and meaningful lives. Communities should work together to increase awareness and education about this critical issue.
Reference
Mental Health Atlas 2020 World Health Organizations https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mental-disorders
National Institute of Mental Health. "Anxiety Disorders." Retrieved from
[https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/anxiety-disorders/index.shtml](https://www.nimh.nih. gov/health/topics/anxiety-disorders/index.shtml)https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/anxiet y-disorders/index.shtml
What's Your Reaction?